String class
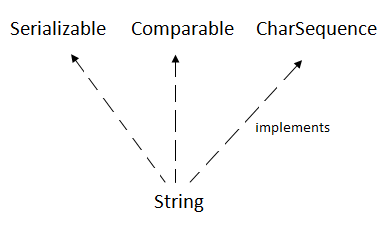
● The java.lang.String class provides a lot of methods to work on string. By the help of these methods, we can perform operations on string such as trimming, concatenating, converting, comparing, replacing strings etc.
● Java String is a powerful concept because everything is treated as a string if you submit any form in window based, web based or mobile application.
toUpperCase() and toLowerCase() method
● The java string toUpperCase() method converts this string into uppercase letter and string toLowerCase() method into lowercase letter.
Syntax:-
String toLowerCase()
String toUpperCase()
Example:-
String s="Sachin";
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());//SACHIN
System.out.println(s.toLowerCase());//sachin
System.out.println(s);//Sachin(no change in original)
String trim() method
● The string trim() method eliminates white spaces before and after string.Syntax:-
String trim()
Example:-
String s=" Sachin ";
System.out.println(s);// Sachin
System.out.println(s.trim());//Sachin
String startsWith() and endsWith() method
● This method has two variants and tests if a string starts with the specified prefix beginning a specified index or by default at the beginning.Syntax:-
boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset)
boolean endsWith(String prefix, int toffset)
Example:-
String s="Sachin";
System.out.println(s.startsWith("Sa"));//true
System.out.println(s.endsWith("n"));//true
String charAt() method
● The string charAt() method returns a character at specified index.Syntax:-
char charAt(int index)
Example:-
String s="Sachin";
System.out.println(s.charAt(0));//S
System.out.println(s.charAt(3));//h
String length() method
● The string length() method returns length of the string. The length is equal to the number of 16-bit Unicode characters in the string.Syntax:-
int length()
Example:-
String s="Sachin";
System.out.println(s.length());//6
String valueOf() method
● The string valueOf() method converts given type such as int, long, float, double, boolean, char and char array into string.Syntax:-
String valueOf(double d)
Example:-
int a=10;
String s=String.valueOf(a);
System.out.println(s+10); //1010
String replace() method
● The string replace() method replaces all occurrence of first sequence of character with second sequence of character.
Syntax:-
String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)
Example:-
String s1="Java is a programming language. Java is a platform. Java is an Island.";
String replaceString=s1.replace("Java","Kava");//replaces all occurrences of "Java" to "Kava"
String substr() method
● This method has two variants and returns a new string that is a substring of this string. The substring begins with the character at the specified index and extends to the end of this string or up to endIndex – 1, if the second argument is given.Syntax:-
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
Example:-
String Str = new String("Welcome to Java SY A"); System.out.println(Str.substring(10, 13) ); //Java
String compareTo() method
● This method compares two strings lexicographically.Syntax:-
int compareTo(String anotherString)
The value 0 if the argument is a string equal to this string; a value less than 0 if the argument is a string greater than this string; and a value greater than 0 if the argument is a string less than this string.
String str1 = "Strings are immutable";
String str2 = "Strings are immutable";
String str3 = "Integers are not immutable";
int result = str1.compareTo( str2 ); //0
System.out.println(result);
result = str2.compareTo( str3 ); //10
System.out.println(result);
result = str3.compareTo( str1 ); //-10
System.out.println(result);
String Buffer class
● The java.lang.StringBuffer class is a thread-safe, mutable sequence of characters. Following are the important points about StringBuffer:● A string buffer is like a String, but can be modified.
● It contains some particular sequence of characters, but the length and content of the sequence can be changed through certain method calls.
● They are safe for use by multiple threads.
● Every string buffer has a capacity.
StringBuffer.capacity() method
● The java.lang.StringBuffer.capacity() method returns the current capacity. The capacity is the amount of storage available for newly inserted characters, beyond which an allocation will occur.● Syntax: int capacity()
StringBuffer.append()
● The java.lang.StringBuffer.append(String str) method appends the specified string to this character sequence.● The characters of the String argument are appended, in order, increasing the length of this sequence by the length of the argument.
● If str is null, then the four characters "null" are appended.
● Syntax:-
StringBuffer append(String str)
StringBuffer.replace()
● The java.lang.StringBuffer.replace() method replaces the characters in a substring of this sequence with characters in the specified String.
● The substring begins at the specified start and extends to the character at index end - 1 or to the end of the sequence if no such character exists.
● First the characters in the substring are removed and then the specified String is inserted at start.
● Syntax:- StringBuffer replace(int start, int end, String str)
StringBuffer.reverse()
● The java.lang.StringBuffer.reverse() method causes this character sequence to be replaced by the reverse of the sequence.● Syntax:-StringBuffer reverse()
StringBuffer.charAt()
● The java.lang.StringBuffer.charAt() method returns the char value in this sequence at the specified index.● The first char value is at index 0, the next at index 1, and so on, as in array indexing.
● The index argument must be greater than or equal to 0, and less than the length of this sequence.
Syntax:- char charAt(int index)
StringBuffer.setCharAt()
● The java.lang.StringBuffer.setCharAt() method sets the character at the specified index to ch.
● This sequence is altered to represent a new character sequence that is identical to the old character sequence, except that it contains the character ch at position index.
● Syntax:-void setCharAt(int index, char ch)
NeXt Artical Related APPLET in Java

Don't Forget to Share your Opinion About This post in Comment Section, Your One Comment Will Not only Make Our day But will Make our Year. And Do mention Of you have any ideas for our Blog:)

0 Comments