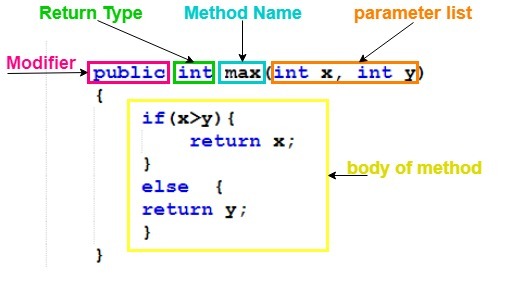
Methods in Java
● Same as functions in programming language● None of the methods can be declared outside the class.
● Why use methods?
– To make code reusable– To parametrise the code
– For top-down programming
– To simplify the code
● Two types of methods
– Instance methods
– Class methods
● Instance methods are used to access/manipulate the instance variables but can also access access class variables.
● Class methods can access / manipulate class variables but cannot access instance variable unless and until they use an object for that purpose.
Method Overloading in Java
● If a class have multiple methods by same name but different parameters, it is known as Method Overloading.
● If we have to perform only one operation, having same name of the methods increases the readability of the program.
● Advantage of method overloading? – Method overloading increases the readability of the program.
● There are three ways to overload the method in java
– By changing number of arguments
– By changing the data type
– By changing the sequence
Access Specifiers in Java
● There are two types of modifiers in java: access modifiers and nonaccess modifiers.● The access modifiers in java specifies accessibility (scope) of a data member, method, constructor or class.
● There are 4 types of java access modifiers:
– Private
– Default
– Protected
– Public
● There are many non-access modifiers such as static, abstract, synchronized, native, volatile, transient etc.
1).Private access modifier
● The private access modifier is accessible only within class.● Role of Private Constructor – If you make any class constructor private, you cannot create the instance of that class from outside the class.
● A class cannot be private or protected except nested class.
2).Default access modifier
● If you don't use any modifier, it is treated as default by default● The default modifier is accessible only within package.
3).Protected access modifier
● The protected access modifier is accessible within package and outside the package but through inheritance only.● The protected access modifier can be applied on the data member, method and constructor.
● It can't be applied on the class.




0 Comments