
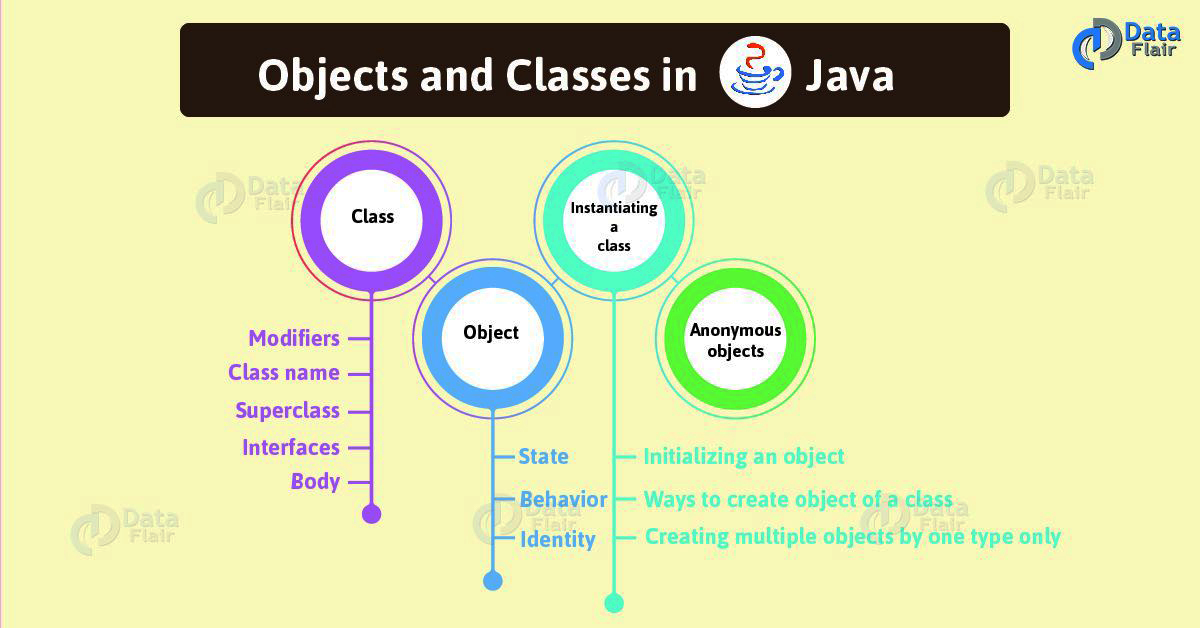
Data Input
● There are 2 ways to take input in Java
– JOptionPane class Click To More Details.
– Scanner class
Scanner Class Terminal:-
● The java.util.Scanner class is a simple text scanner which can parse primitive types and strings using regular expressions.
● This Scanner class is found in java.util package.
● Following are the important points about Scanner:
– The Java Scanner class breaks the input into tokens using a delimiter that is white space.
– Java Scanner class is widely used to parse text for string and primitive types using regular expression.
– A Scanner is not safe for multithreaded use without external synchronization.
● How to Input:-
int n;
n = s.nextInt(); // s is object of Scanner class
Statement n = s.nextInt(); is used to input the value of an integer variable 'n' from the user.
Statement n = s.nextInt(); is used to input the value of an integer variable 'n' from the user.
Here, nextInt() is a method of the object s of the Scanner class.
*Most Important Part Of Scanner Class
Method Inputs
nextInt() Integer
nextFloat() Float
nextDouble() Double
nextLong() Long
nextShort() Short
next() Single word
nextLine() Line of Strings
nextBoolean() Boolean
- The only difference between the methods nextLine() and next() is that nextLine() reads the entire line including white spaces, whereas next() reads only upto the first white space and then stops.
Example:-
// Java program to read data of various types using Scanner class.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ScannerDemo1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declare the object and initialize with
// predefined standard input object
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// String input
String name = sc.nextLine();
// Character input
char gender = sc.next().charAt(0);
// Numerical data input
// byte, short and float can be read
// using similar-named functions.
int age = sc.nextInt();
long mobileNo = sc.nextLong();
double cgpa = sc.nextDouble();
// Print the values to check if the input was correctly obtained.
System.out.println("Name: "+name);
System.out.println("Gender: "+gender);
System.out.println("Age: "+age);
System.out.println("Mobile Number: "+mobileNo);
System.out.println("CGPA: "+cgpa);
}
}
Out Put IS Compile The Code:-


0 Comments